Functional annotation of a novel toxin-antitoxin system Xn-RelT of Xenorhabdus nematophila; a combined in silico and in vitro approach
Abstract
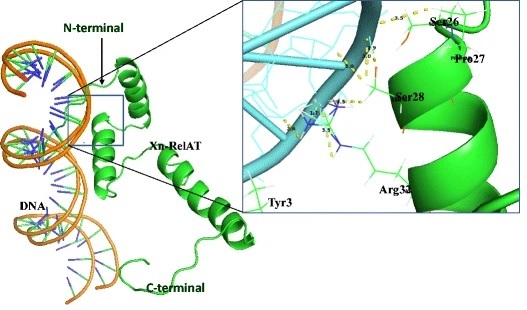
Toxin-antitoxin (TA) complexes play an important role in stress responses and programmed cell death in bacteria. The RelB-RelE toxin antitoxin system is well studied in Escherichia coli. In this study, we used combined in silico and in vitro approaches to study a novel Xn-RelT toxin from Xenorhabdus nematophila bearing its own antitoxin Xn-RelAT - a RelB homolog of E. coli. The structure for this toxin-antitoxin pair is yet unknown. We generated homology-based models of X. nematophila RelT toxin and antitoxin. The deduced models were further characterized for protein-nucleic acid, protein-protein interactions and gene ontology. A detrimental effect of recombinant Xn-RelT on host E. coli was determined through endogenous toxicity assay. When expressed from a isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside-regulated LacZ promoter, Xn-RelT toxin showed a toxic effect on E. coli cells. These observations imply that the conditional cooperativity governing the Xn-RelT TA operon in X. nematophila plays an important role in stress management and programmed cell death.